What is an LLMNR, and how does it relate to DNS?
When it comes to computer networks, two important terms often come up: LLMNR (Link-Local Multicast Name Resolution) and DNS (Domain Name System). Both are used to resolve names to IP addresses, but they work in different ways. Let’s break them down in a simple way.
What is LLMNR?
LLMNR (Link-Local Multicast Name Resolution) is a protocol used by computers to find each other on small local networks. It is mainly used when a DNS server is unavailable or when a device does not have a DNS entry.
Here’s how LLMNR works:
- When a computer wants to find another device on the same network, it sends a request to all nearby devices.
- The computer that has the matching name responds with its IP address.
- The requesting computer then connects to it.
LLMNR is mainly used in home networks, small offices, or situations where there is no central DNS server.
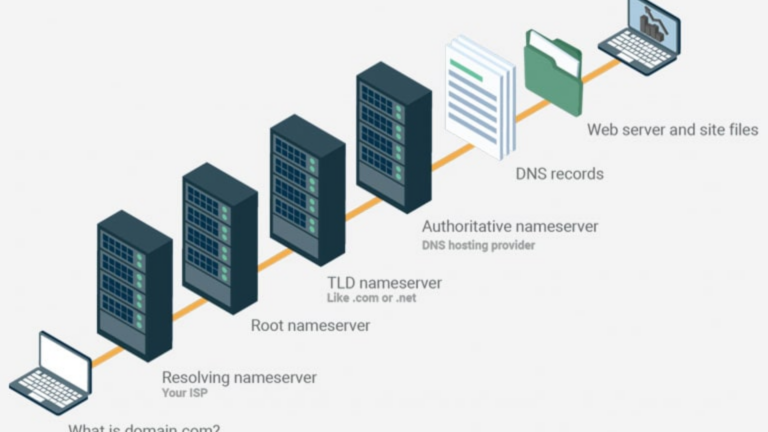
What is DNS?
DNS (Domain Name System) is the primary system used to match domain names (like google.com) to IP addresses (like 192.168.1.1). It is essential for the internet to work properly.
How DNS works:
- You type a website address in your browser.
- Your computer sends a request to a DNS server.
- The DNS server finds the IP address linked to that domain name.
- Your computer connects to the correct server to load the website.
Key Differences Between LLMNR and DNS
| Feature | LLMNR | DNS |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Local network only | Internet and large networks |
| Server Needed? | No | Yes |
| Speed | Fast in small networks | Efficient for large networks |
| Usage | Finding devices on local networks | Finding websites and servers across the internet |
When is LLMNR Used Instead of DNS?
LLMNR comes in handy when:
- There is no DNS server available.
- Devices need to communicate on a small, local network.
- You are setting up a new network and devices need to discover each other automatically.
However, LLMNR is not a replacement for DNS because it does not work well on large networks or the internet.
Should You Disable LLMNR?
In some cases, network administrators disable LLMNR because it can create security risks. Hackers can trick devices into connecting to a fake IP address. If you are in a secure office or corporate environment, it might be a good idea to turn off LLMNR and rely only on DNS.
Final Thoughts
LLMNR and DNS both help computers find the right IP addresses, but they serve different purposes. LLMNR is useful for small local networks where DNS is not available, while DNS is essential for accessing the internet. Understanding when and how to use each one can help improve network performance and security.