What are the pros and cons of using encrypted DNS?
The internet is something we use every day, but most people don’t think about how it actually works. One important part of the internet is the Domain Name System (DNS).
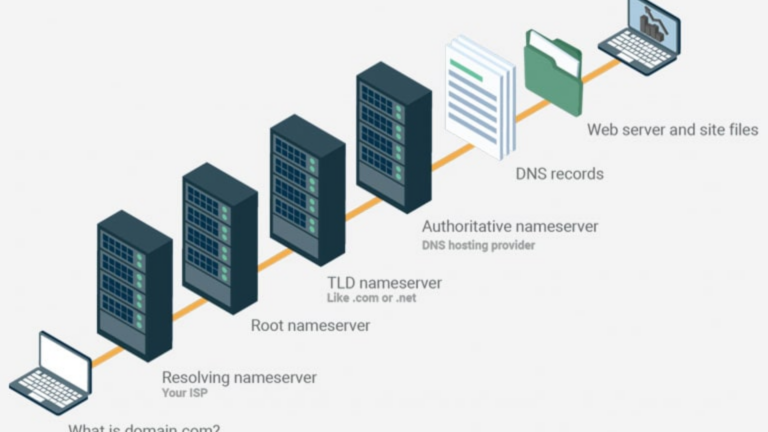
DNS helps translate website names (like google.com) into the numbers (IP addresses) that computers use to find websites.
Normally, DNS queries are sent in a way that anyone on the network can see them. This means hackers, internet providers, or even governments can track what websites you visit. To improve privacy, encrypted DNS was introduced. But is it always a good thing? Let’s take a look at the pros and cons.
What Is Encrypted DNS?
Encrypted DNS is a way to hide your DNS requests so that no one can easily see which websites you are trying to visit. It works by using secure methods like DNS over HTTPS (DoH) or DNS over TLS (DoT) to keep your data private.
Now, let’s explore the benefits and drawbacks of using encrypted DNS.
Pros of Using Encrypted DNS
1. Better Privacy
With encrypted DNS, your internet provider, hackers, or anyone else snooping on your connection cannot easily see which websites you visit.
This adds an extra layer of privacy when you browse the internet.
2. Improved Security
Since regular DNS requests are open for anyone to see, hackers can trick you into visiting fake websites (this is called DNS spoofing).
Encrypted DNS helps prevent these types of attacks by making sure your requests stay safe.
3. Stops ISP Tracking
Many internet service providers (ISPs) track your browsing habits and may even sell this data to advertisers. Encrypted DNS makes it harder for them to monitor what you are doing online.
4. Works Well on Public Wi-Fi
When using free Wi-Fi at a coffee shop, airport, or hotel, hackers can easily spy on your internet activity. Encrypted DNS protects you from this by keeping your browsing data private.
5. Prevents Some Internet Restrictions
In some countries, governments block certain websites by filtering DNS requests. Encrypted DNS can sometimes bypass these restrictions, giving you access to websites that might otherwise be blocked.
Cons of Using Encrypted DNS
1. Can Slow Down Internet Speed
Since encrypted DNS adds extra security layers, it can sometimes take longer for websites to load. This may not be noticeable in most cases, but for some people, it could be a small drawback.
2. May Not Work on All Devices
Some older devices and networks don’t support encrypted DNS, which means you might have trouble using it in certain situations.
3. Harder to Monitor for Parents or Businesses
Many parents use DNS filters to block harmful or inappropriate websites for their children. Similarly, businesses use DNS to control what employees can access.
Encrypted DNS can make it harder to enforce these filters.
4. Might Not Always Be Fully Secure
While encrypted DNS protects your requests, it does not hide everything. For example, websites still know your IP address, and your internet provider can still see that you are connected to certain services.
5. Some Websites or Services May Block It
Certain companies or governments block encrypted DNS to maintain control over what users can access. If your network does not allow encrypted DNS, you may have trouble connecting to some websites.
Should You Use Encrypted DNS?
If privacy and security are your main concerns, encrypted DNS is a great option. It keeps your browsing habits private and protects against certain online threats.
However, if you rely on parental controls, have an older device, or experience slow internet speeds, you might want to think carefully before enabling it.
The good news is that most modern browsers and devices give you the choice to turn encrypted DNS on or off. If you’re unsure, you can try it and see if it works well for your needs.
Conclusion
Encrypted DNS is a useful tool that helps protect your online privacy and security. However, it also has some downsides, like potential speed issues and difficulties with parental controls.
Before using it, consider both the pros and cons to decide if it’s right for you.