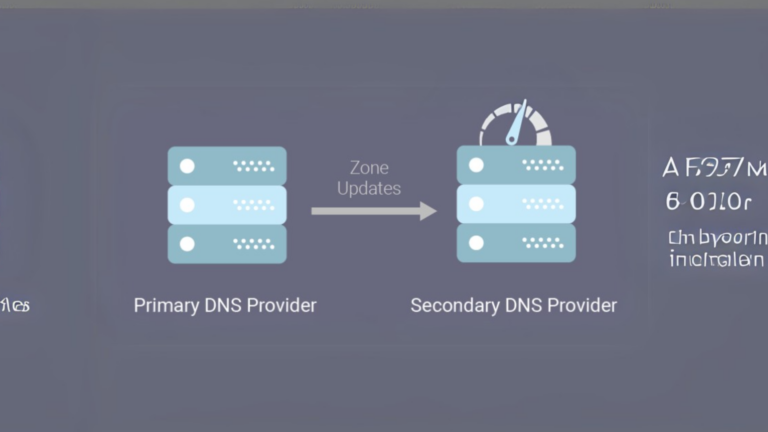
What are the challenges of managing DNS in large enterprises?
Managing DNS (Domain Name System) in a large enterprise is not as simple as handling a personal website or a small business. DNS plays a crucial role in keeping websites, internal applications, and communication systems running smoothly.
If DNS is not properly managed, it can lead to downtime, security risks, and performance issues. Here are some of the main challenges enterprises face when handling DNS.
1. Scalability Issues
Large enterprises have thousands of employees, multiple offices, and a vast number of devices connected to their network. Managing DNS for such a large infrastructure requires:
- Handling a high volume of DNS queries.
- Ensuring DNS servers can handle increasing demand.
- Keeping DNS records updated as the company grows.
2. Security Risks
DNS is a common target for cyberattacks, and large enterprises are at higher risk. Some of the major security concerns include:
- DNS Spoofing (Cache Poisoning): Attackers manipulate DNS records to redirect users to fraudulent websites.
- DDoS Attacks: Hackers flood DNS servers with traffic, causing them to crash.
- Data Exfiltration: Attackers use DNS to steal sensitive data without detection.
To reduce these risks, enterprises need strong security measures, such as DNS firewalls, DNSSEC (DNS Security Extensions), and constant monitoring.
3. Complexity in Managing Multiple Locations
Enterprises with offices in different regions often need separate DNS configurations for each location. This creates challenges such as:
- Ensuring employees can access the correct local servers.
- Managing different DNS providers or settings for various regions.
- Keeping all DNS records consistent across locations.
4. Keeping DNS Records Accurate
Large enterprises frequently update their websites, add new services, and change IP addresses. Each change requires updates to DNS records.
If records are outdated or incorrect, it can cause:
- Websites and applications to become unreachable.
- Email communication failures.
- Slower network performance.
Proper documentation and automated DNS management tools can help prevent these issues.
5. Managing Internal and External DNS
Enterprises often use DNS not just for public websites but also for internal applications, like email servers and cloud services.
This means they have to manage both external and internal DNS, which can be complicated because:
- Internal DNS must remain secure and private.
- External DNS must be accessible to customers and partners.
- Misconfigurations can lead to data leaks or downtime.
6. Compliance and Legal Regulations
Many industries have strict rules about data privacy and security. Some regulations, such as GDPR, require enterprises to keep DNS data protected. Compliance challenges include:
- Ensuring DNS logs do not expose sensitive data.
- Following country-specific rules about data storage.
- Regular audits to ensure compliance with security policies.
7. Cost of Infrastructure and Maintenance
Maintaining a reliable DNS infrastructure requires investment in:
- High-performance DNS servers.
- Security solutions to prevent attacks.
- Skilled IT staff to manage and monitor DNS.
For cost efficiency, some enterprises use cloud-based DNS services, while others prefer in-house solutions for better control.
Conclusion
DNS management in large enterprises is complex and requires careful planning. Security risks, scalability issues, and the need for accurate record-keeping make it a challenging task.
However, with the right tools, automation, and security measures, enterprises can ensure their DNS runs smoothly, keeping their systems online and secure.